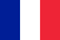
The lumbar region has more load than all other parts of the spine. Osteochondrosis develops as a result of degenerative-dystrophic processes due to a decrease in disc height. Marginal osteophytes develop along the edges of the vertebrae. At the same time, the intervertebral foramen narrows, the roots are compressed, and symptoms of osteochondrosis appear. Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis depends on the stage of the disease.
Osteochondrosis sometimes manifests itself in such a way that its symptoms "mimic" damage to other organs. He has allocated a code in the ICD - 10. We will try to understand all the intricacies in more detail.
International classification
According to ICD-10, osteochondrosis has the code M42 and is divided into subspecies. Code M42. 0, according to ICD-10, indicates that this is a young variant, osteochondrosis is indicated by Scheuermann-Mao or Calve disease. Code M42. 1 according to ICD-10 gives a picture of the disease in adults.
If the disease variant is not specified, then in the ICD-10 the code is M42. 9. There are also complications of childhood osteochondrosis, the ICD-10 code is completely different for them. Complications occur in the form of juvenile kyphosis, which gives Scheuermann-Mao disease. The code is according to ICD-10 M40. 0.
Because of the appearance
Why everything appears is not yet fully known, one thing has been fixed for sure: a violation of the structure of the intervertebral disc develops, which leads to further changes in the spine. Symptoms can be clearly seen after 35 years, accelerate the process of injury, long stay in a static position, due to the load. But it’s not just the burden that is to blame, often the disease is genetic. The cause may be flat feet, especially grade 3 or 4.
symptoms
The peculiarity of this spinal disease is undeniable, and over time it only develops. Overall, doctors distinguish four degrees of development of this pathology.
The first degree does not give any pain, a person can sit calmly and without pain, but changes in the characteristics of the disease already occur in the core of the intervertebral disc. The ligaments that strengthen the vertebrae can also suffer. Locally, discomfort can be observed, which is able to give away from problem areas. As a result of violations of the conservation of vessels on the bottom of the legs, they become cold.
In the second stage, destruction of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc occurs. Instability appears in the lumbar spine, increased mobility and local tension of the lumbar muscles can be observed. One feels constant fatigue, discomfort in the back and a sense of insecurity.
In the third stage, osteochondrosis leads to the fact that the fibrous ring completely loses its strength and ruptures, the nucleus pulposus, in turn, goes beyond it, so a hernia is formed. There is compression of the spinal nerve roots, symptoms develop, especially pain. In the conservation zone of the compressed nerve root, sensitivity is completely or partially lost. Morning or daily exercise brings significant pain. In the early stages, a burning sensation, annoying tingling, then the turn of numbness comes. Decreased or lack of sensitivity can be considered a cause of paralysis, resulting in muscle atrophy.
According to the characteristic zone of sensitivity deterioration, it can be assumed in which part the failure occurs. If the sciatic nerve fibers (thickest in the body) are affected, Lasègue’s symptoms will be positive, easy to check at home. It is necessary to lie on your back, the stranger helps to raise the legs straight at the knees upwards. With positive symptoms, the pain will increase if the leg is bent at the knee joint, it disappears completely.
With a significant hernia size, spinal cord function may be impaired. Often you can see symptoms of "ponytail" compression, so osteochondrosis often manifests itself, this is a group of nerves that, leaving the spinal cord, pass through the lumbar and sacral spine. Symptoms are indicated by impaired movement and sensitivity of the lower leg. In addition, the dysfunction of the pelvic organs is added, often this is the bladder.
In the fourth stage, the intervertebral joints and ligaments are involved in a degenerative process, and symptoms of spinal instability appear. Arthrosis of the joints between the vertebrae, spondylarthrosis develops. There is almost no pain at this stage, but along with this, the ability to move in it, training or gymnastics for a person is almost completely lost and becomes a real problem.
Due to the defeat of various nerves that invade internal organs, their function may be impaired. Sometimes for a long time a person struggles with one problem, but in fact the cause is osteochondrosis. In addition to the fact that there are characteristic symptoms, spinal osteochondrosis must be established instrumentally.
Diagnostics
The symptoms are important, but additional confirmation of osteochondrosis allows a picture of the lumbar spine. It shows damage to the vertebral joints, decreased disc height, narrowing of the intervertebral foramen. Spinal images were taken in two projections, additional functional testing may be required.
You can confirm the presence of a disc hernia with MRI, the image will show characteristic changes. CT will show the structure of the tissue more clearly, it is very convenient because the technique is done in different planes and sections. It is possible to consider the place where the symptoms arise and are disturbed.
Treatment
Before treating lumbar osteochondrosis, consultation with a neurologist is necessary. Medications are always effective in helping to get rid of the disease. They are set in a course for about 10 days, completing all physiotherapy, daily exercises, gymnastics, massage.
With the help of medications, you can eliminate severe pain caused by inflammation and swelling effectively. After treatment in the hospital, taking medications and according to the doctor's prescription can be continued at home.
Everyone starts with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs. Due to the fact that they reduce the inflammatory process in osteochondrosis, swelling and pain disappear. Doctors are involved in the selection of drugs: they have many contraindications. But along with this, they quickly allow to alleviate the condition, after a few days a person will get rid of the pain and will sit as usual, osteochondrosis will subside.
Treatment will be lower if you do not use medications aimed at restoring cartilage structure. They are called chondroprotectors and contribute to better cartilage nutrition, recovery of disc tissue at an early stage. You have to take it for a long time, even at home.
Muscle relaxation makes it possible to relieve spasms of the muscles of the lower back. This condition is a response to root compression.
Medicines that increase microcirculation are needed. All of this will eliminate the swelling in the area where the compression occurs, giving the nerve cells more oxygen and nutrients. Exercise and massage have the same effect, which can be done at home to relieve pain.
If your back is very sore and sitting becomes a real problem, analgesics will be needed. This group of drugs will quickly get rid of the manifestations of the disease.
Vitamins improve the nutrition of nerve roots, strengthen them. With the use of this group of drugs, treatment is more effective. Perfectly overcomes the symptoms of pain ointment, which must be applied at the place of maximum pain.
The doctor prescribes an ointment if the back is very sore and it is impossible to sit up. Penetrating into the tissues, the ointment has an anti-inflammatory effect on the roots. You can apply the ointment in the form of compresses at night. Apply the ointment to the sore area three times a day.
Physiotherapy
Complete rehabilitation treatment consists of:
- physiotherapy training;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- attraction;
- manual therapy;
- reflexology.
Therapeutic gymnastics consists of applying a dosing load on the lumbar spine. With its help, the clamped roots are released, the muscles are strengthened, the correct posture is established, which is then supported by charging. Gymnastics allows you to increase the range of motion, making the ligaments more elastic. Gymnastics is chosen individually for each person.
These techniques, like charging, are easy to perform, contribute to the normalization of blood circulation, and increase metabolism. Gymnastics helps improve the nutrition of the intervertebral discs, increasing the space between the vertebrae. Due to the formation of the corset, the pain and load on the spine is reduced. Gymnastics is performed under the supervision of a specialist, and charging is required every morning, it will prevent osteochondrosis.
Physiotherapeutic methods used, as well as charging, are very widespread. Especially low frequency current, alternating current, ultrasound, laser and many more aids. With ultrasound, you can also use an ointment. Methods of relieving inflammatory processes, pain and swelling. Most popular:
- UHF;
- diodynamics;
- magnet;
- shock wave therapy;
- ultrasound;
- electrophoresis.
Massage is very often used on stages when possible to relieve pain. Massage, like exercise, promotes cartilage nutrition, improves metabolic processes. It is a combined sequence of special techniques: rubbing, kneading, rubbing and shock vibration.
Properly done massage is the key to successful treatment and subsequent recovery. Massage can only be done by a specialist. In addition, you can use ointments with anti-inflammatory effect. Massage allows you to relieve muscle spasms, increase blood flow, strengthen the back.
Manual therapy is also a massage, using only special techniques. The effect is the same as the sequence.
With the help of weights and specially selected techniques, traction is performed. This procedure helps to increase the space between the vertebrae, relieve pain, restore the anatomical axis of the spine.
Acupuncture is based on the effect of a needle puncture on the active point of the human body. This technique is indicated primarily for severe pain syndromes.